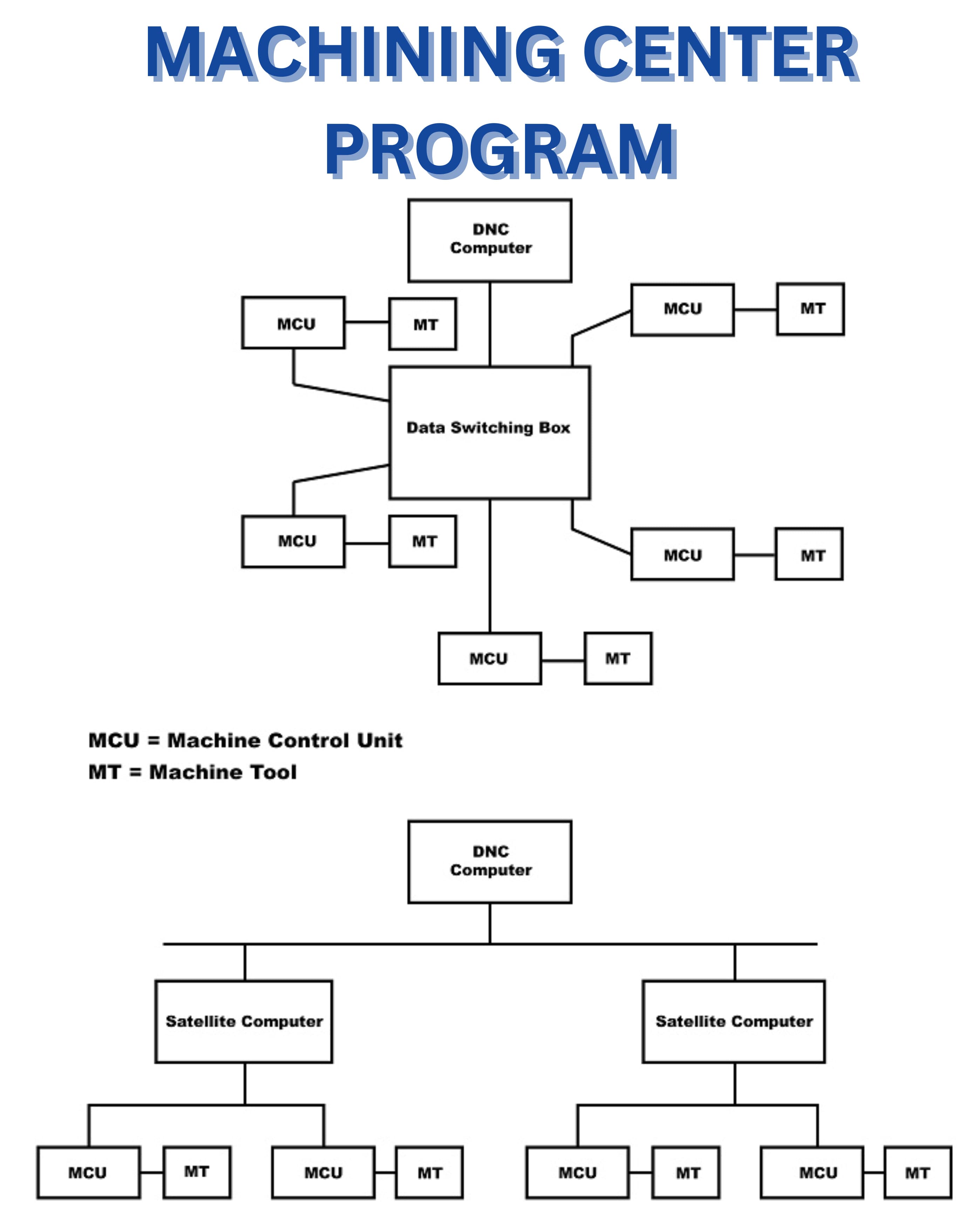
MACHINING CENTER PROGRAM
Other Chapters
INTRODUCTION TO NUMERICAL CONTROLNC MACHINE TOOL CHARACTERISTICSTYPES OF MACHINE TOOLSCONFIGURATION AND CONTROL METHOD OF NC MACHINE TOOLSACCESSORIES TOOLS AND CUTTING FLUIDTURNING CENTER PROGRAMMACHINING CENTER PROGRAMAUTOMATED MANUFACTURING SYSTEMCONDITION FOR CUTTINGCUTTING TOOLS AND CHIPSSELECTING A TYPE OF TOOL MATERIAL
- Q1: Define Machining Process.Ans: Machining process is a material removal process in which a cutting tool removes material from a workpiece to obtain the desired shape and dimensions.
- Q2: Write the steps for the Machining Process.Ans: The steps for the Machining Process are as follows:
- ➔ First, carefully study the part drawing to understand the required shape and dimensions.
- ➔ Select the appropriate machine and cutting tools based on the material and operations.
- ➔ Securely fix the workpiece on the machine to ensure stability during machining.
- ➔ Set up the machining parameters or program the machine as needed for the operation.
- ➔ Execute the machining operations to remove material and form the desired shape.
- ➔ Inspect the finished part to verify accuracy, dimensions, and surface finish.
- Q3: Define Part Drawing.Ans: A part drawing is a technical document that shows the dimensions, tolerances, and details required to manufacture a component.
- Q4: Define Pallet?Ans: A pallet is a platform used to hold and transport workpieces in a machining center.
- Q5: Define Program Number.Ans: A program number is a unique identifier assigned to a CNC program for easy selection and execution.
- Q6: Define Sequence Number.Ans: A sequence number is a number given to each line of CNC code to maintain the order of execution.
- Q7: Define Work C-ordinate System.Ans: Work coordinate system defines the origin point on the workpiece from which all machining movements are measured.
- Q8: How many tools can be accommodated in a machining center? How are they mounted?Ans:
- ➔ The number of tools depends on the machine design (typically 12 to 60 tools)
- ➔ Tools are mounted on the tool magazine or turret for automatic selection
- Q9: For what purpose canned cycles are used?Ans: Canned cycles are used to simplify repetitive machining operations like drilling, boring, or tapping by using a single command.
- Q10: Briefly narrate the tool length compensation.Ans: Tool length compensation adjusts the machine to account for the length of the cutting tool so that the programmed dimensions are accurate.
- Q11: When will the G03 code be used?Ans: G03 code is used for circular interpolation in counter-clockwise (CCW) direction.
- Q12: When will the G42 code be used?Ans: G42 code is used for tool radius compensation on the right side of the programmed path.
- Q13: When will the G80 code be used?Ans: G80 code is used to cancel canned cycles.
- Q14: When will the G91 code be used?Ans: G91 code is used for incremental programming where movements are measured from the current position.
- Q15: When will the G92 code be used?Ans: G92 code is used to set the workpiece coordinate system offset or specify a feed rate limit.
- Q16: When will the G98 code be used?Ans: G98 code is used to return to the initial plane after a canned cycle in drilling operations.
- Q17: When will the M02 code be used?Ans: M02 code is used to end the CNC program.
- Q18: When will the M04 code be used?Ans: M04 code is used to start the spindle in counter-clockwise (CCW) direction.
- Q19: When will the M06 code be used?Ans: M06 code is used to change the tool automatically.
- Q20: When will the M09 code be used?Ans: M09 code is used to turn OFF the coolant.
- Q21: When will the M43 code be used?Ans: M43 code is used to control auxiliary functions such as turning ON/OFF secondary devices.
- Q22: When will the M99 code be used?Ans: M99 code is used to end a subprogram or return to the main program.