CAM (COMPUTER AIDED MANUFACTURING)
Other Chapters
INTRODUCTION TO 2D AND 3D CAD2D SKETCHES (ASTM STANDARDS)DIMENSIONS AND CONSTRAINTS (ASTM STANDARDS)TOLERANCES (ASTM STANDARDS)SOLID MODELINGASSEMBLY MODELINGDRAWING VIEWPRESENTATION MODULESHEAR METAL COMPONENTSCAM (COMPUTER AIDED MANUFACTURING)PROCESS PLANNING
- Q1: Define CAM.Ans: CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) is the use of software to control machine tools and automate manufacturing processes.
- Q2: What is CAM used for?Ans: CAM is used to generate tool paths, control machines, and manufacture parts accurately and efficiently.
- Q3: Define User Interface.Ans: User Interface in CAM is the platform where users interact with the software to design, simulate, and control machining operations.
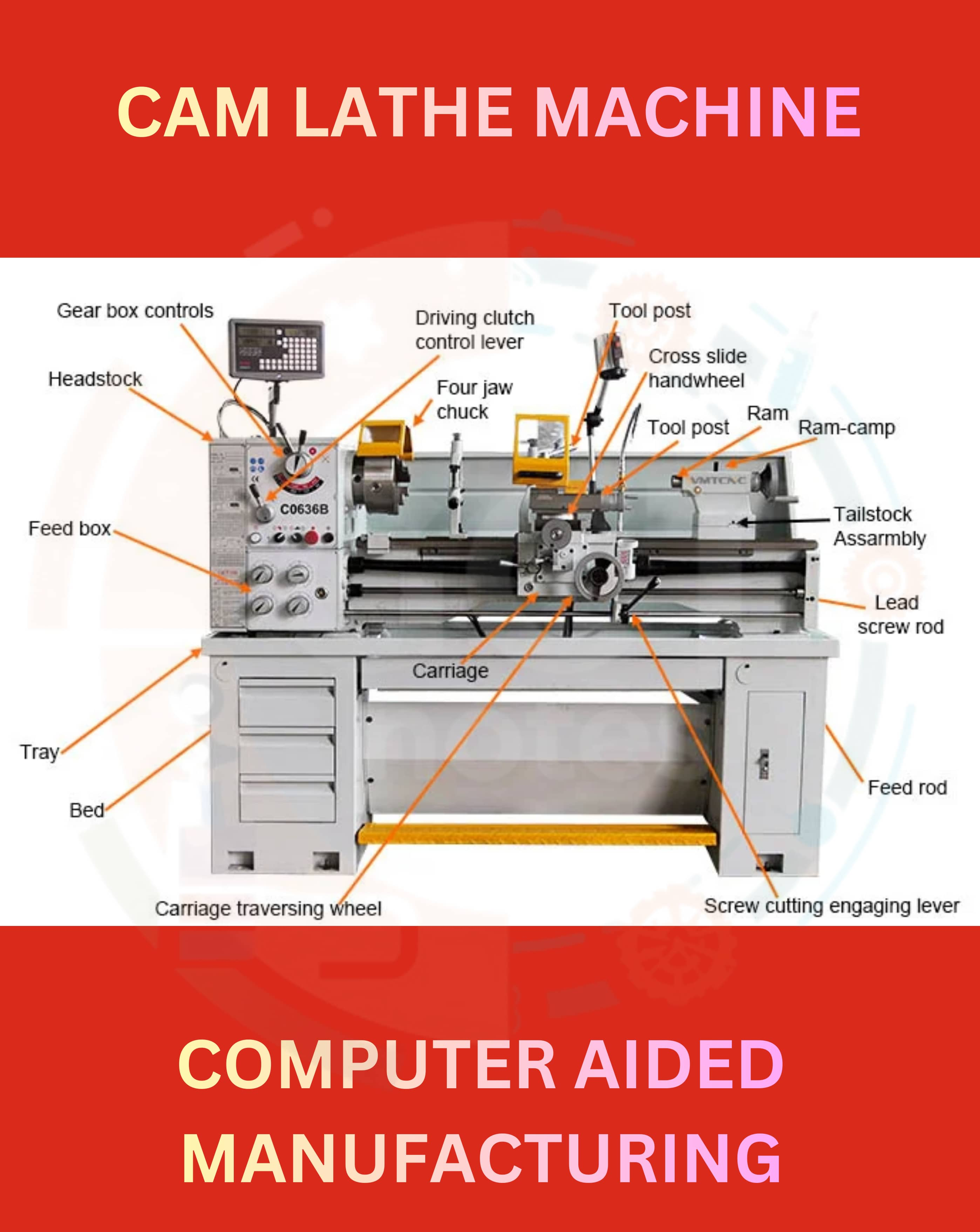
- Q4: Describe CAM Lathe.Ans: CAM Lathe is a machining operation used for turning cylindrical parts, cutting, and shaping them on a lathe machine.
- Q5: Define Boring.Ans: Boring is the process of enlarging or finishing an existing hole using a single-point cutting tool.
- Q6: Describe the CAM router.Ans: CAM Router is used to cut, engrave, or carve materials like wood, plastics, or metal sheets using CNC routing machines.
- Q7: List down the operations performed with CAM Lathe.Ans: Operations performed with CAM Lathe are as follows:
- ➔ Facing
- ➔ Turning
- ➔ Boring
- ➔ Threading
- ➔ Grooving
- ➔ Drilling
- Q8: Define 4 Axis Milling.Ans: 4 Axis Milling allows the tool to move along X, Y, Z axes and rotate around the A-axis for complex shapes.
- Q9: Define 5 Axis Swarf Milling.Ans: 5 Axis Swarf Milling uses 5 axes to machine surfaces at precise angles using the side of the cutter.
- Q10: Define 5 Axis Index Drilling.Ans: 5 Axis Index Drilling drills holes at different angles by rotating the part along two additional axes.
- Q11: Define Parallel Roughing.Ans: Parallel Roughing removes large amounts of material in parallel passes to shape the rough part quickly.
- Q12: Define Plunge Roughing.Ans: Plunge Roughing removes material by moving the cutter vertically down into the material repeatedly.
- Q13: Define Flat Roughing.Ans: Flat Roughing machines horizontal surfaces using multiple passes to remove material evenly.
- Q14: Define Finish Cutting.Ans: Finish Cutting is the final machining operation to give a part its accurate dimensions and smooth surface finish.
- Q15: Define Cutting tools in CAM.Ans: Cutting Tools are tools like end mills, drills, or lathes used in CAM to remove material from a workpiece.
- Q16: How to setup Cutting tools in CAM.Ans: The procedure to setup cutting tools is as follows:
- ➔ Select the tool library in CAM software.
- ➔ Choose the required cutting tool.
- ➔ Define tool parameters like diameter, length, and speed.
- ➔ Assign the tool to the specific operation.
- ➔ Confirm and save the setup.
- Q17: Define 2D CAM.Ans: 2D CAM creates tool paths on a flat plane (X and Y axes) for simple cutting operations like engraving or profile cutting.
- Q18: Define Side Cutting in CAM.Ans: Side Cutting removes material from vertical faces using the side of the cutting tool.
- Q19: Define Face Cutting in CAM.Ans: Face Cutting removes material from the top surface of the workpiece to make it flat or smooth.
- Q20: Define Pocket Cutting in CAM.Ans: Pocket Cutting removes material from a recessed area to create cavities or pockets in a part.
- Q21: Define Slot Cutting in CAM.Ans: Slot Cutting removes material along a narrow path to create slots or channels in a workpiece.
- Q22: Define CAM Milling.Ans: CAM Milling is the process of machining parts using a rotating cutter controlled by CAM software.
- Q23: Define Rough Cutting.Ans: Rough Cutting removes large amounts of material quickly to shape a part before finishing.
- Q24: Define Z Level Roughing.Ans: Z Level Roughing removes material layer by layer along the Z-axis to create the rough shape.
- Q25: Define Leads and Stepovers.Ans: Leads and Stepovers control how the cutter enters the material and moves between passes to ensure smooth cutting.
- Q26: Define Parallel Finishing.Ans: Parallel Finishing machines the surface with parallel passes to produce a smooth finish.
- Q27: Define Z-Level Finishing.Ans: Z-Level Finishing machines vertical walls and steep surfaces layer by layer to achieve a fine finish.
- Q28: Define Corner and Pencil Finishing.Ans: Corner and Pencil Finishing machines tight corners or small radii that standard finishing passes cannot reach.
- Q29: Define Isoline Finishing.Ans: Isoline Finishing machines a surface by following its contour lines for a smooth finish.
- Q30: Define Radial and Spiral Finishing.Ans: Radial and Spiral Finishing machines surfaces using circular or spiral tool paths for smooth contours.
- Q31: Define Flow Line Finishing.Ans: Flow Line Finishing follows the natural flow of the surface for a uniform finish.
- Q32: Define Between Two Curve Finishing.Ans: Between Two Curve Finishing machines the surface between two defined curves to achieve precision.
- Q33: Define Step Over Finishing.Ans: Step Over Finishing moves the cutter incrementally between passes to finish flat or gently curved surfaces.
- Q34: Define Swarf Finishing.Ans: Swarf Finishing machines the side of the cutter along angled surfaces for precise finishing.
- Q35: Define Facing.Ans: Facing is a cutting operation that machines the top surface of a part to make it flat.
- Q36: Define Threading.Ans: Threading is the process of cutting helical grooves on a cylindrical surface to create threads.
- Q37: Define Grooving.Ans: Grooving is the process of cutting narrow slots or channels on a part using CAM tools.
- Q38: What is CAM Wire cut?Ans: CAM Wire Cut is a process that uses a wire electrode to cut precise shapes in conductive materials.
- Q39: Define Die Cutting.Ans: Die Cutting uses a shaped tool or die to cut specific patterns or shapes from a material sheet.
- Q40: Define Punch Cutting.Ans: Punch Cutting uses a punch tool to create holes or shapes by pushing through the material.
- Q41: Define Taper Cutting.Ans: Taper Cutting machines surfaces at a specific angle instead of vertical to create tapered parts.
- Q42: Define No core Cutting.Ans: No core Cutting removes material completely without leaving any central core or leftover.
- Q43: Define Axis Wire Cutting.Ans: Axis Wire Cutting uses multiple axes to control the wire path for complex 3D shapes.
- Q44: Define Nesting.Ans: Nesting arranges multiple parts efficiently on a material sheet to minimize waste.
- Q45: Define Pocketing.Ans: Pocketing removes material inside a closed boundary to create pockets or cavities.
- Q46: Define Engraving.Ans: Engraving is the process of cutting or carving text, logos, or patterns into a material.